Duration: 2006-2008
Acopian Center for the Environment
Yerevan State University
State Pedagogical University
Birds of prey are excellent environmental indicators and flagship species for natural-resource conservation. Increasing of Armenian agriculture and other branches of industry can have a negative impact on the environment. To track the possible influence of industry to our nature we would like to start monitoring of subpopulations of model species in some regions of Armenia.
As a species to be monitored we have chosen Long-legged Buzzard (Buteo rufinus) because it is the most common rodent-eating bird that breeds in whole Armenia.
It will include mapping of nests and a survey of reproductive success. In 2006 we will conduct a pilot survey to see how many nests we can find.
Then in 2007 and later on we will investigate their feeding, reproductive success and analyze collected data on GIS Arc View.
The project will include education of local inhabitants about the importance of rodent-eating raptors for agriculture and nature ecosystems.
The surveys were conducted by students, who have completed BITC courses in AcopianCenter for the Environment.
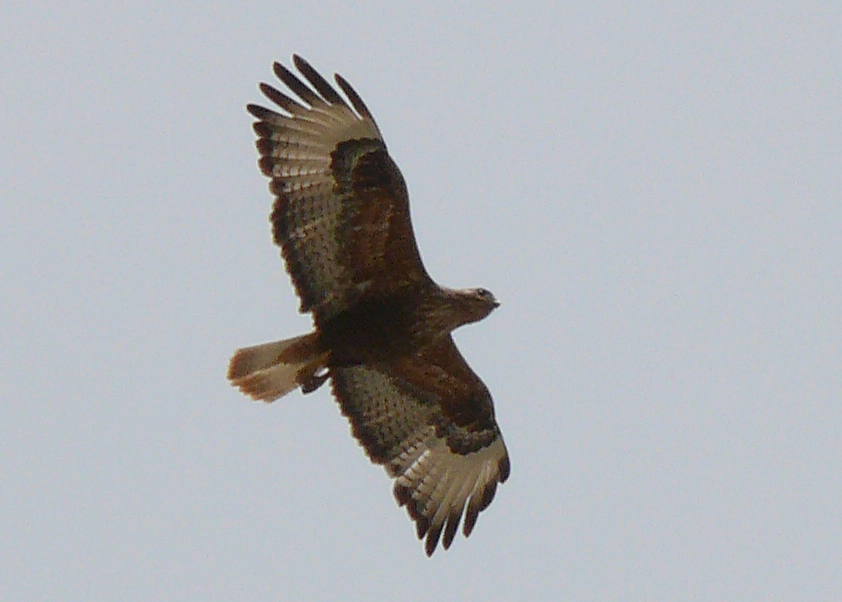

Long-legged Buzzard Buteo rufinus, outskirts of Gusana village, Shirak region of Armenia, Sep 9, 2005.
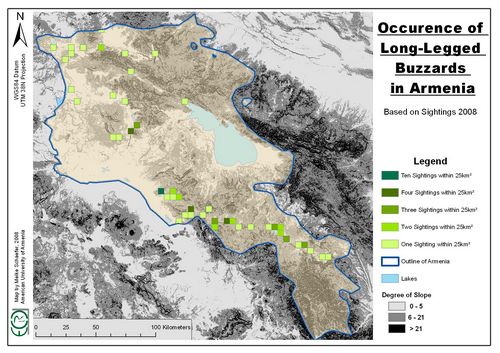
Distribution map of the Long-legged Buzzard Buteo rufinus in Armenia
Results:
The Long-legged Buzzard (hereinafter LLB, Buteo rufinus) in Armenia was studied during 2006-2008 in frames of general bird survey trips and special trips aimed searching of the LLB nests. The study area covers some districts in the central part of Armenia. The distances between the nests (nearest neighbor distance) vary in different regions of Armenia: in Vedi district, the mean distance is 1.98±0,19km (n=10) while in Vayots Dzor region the mean distance is 3.04±0.3km (n=5); t=3.14, p=0.008. The difference in density seems correlated with the steepness of the surrounding area, since the Vedi district is generally flatter than the Vayots Dzor region, which indicates that probably LLB prefers habitats with less steepness of slopes. Most probably it depends on hunting technique of LLB, which catches the prey on the ground dropping down from 5-10m. The other limiting factor is cliff availability since in Armenia LLB breeds only on cliffs. Although LLB does not show dependence on the height of the cliffs and can place the nest on the height from 2 to 30m, it does not breed on trees, like in some parts of its area in Siberia.
The concluding results of the studies will be presented as an article on the International Raptor Conference in autumn 2009 in Switzerland.
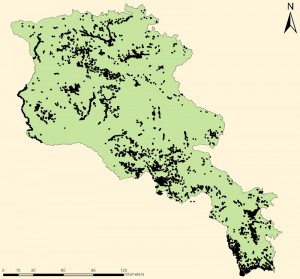
In the frames of the study, a GIS shapefile was developed, covering all cliffs and rocky massifs of the entire territory of Armenia.
Relevant publication:
Some habitat preferences of Long-legged Buzzard (Buteo rufinus) in Armenia
Hovanisyan, T., Janoyan, G., Schaefer, M., Aghababyan, K.